We have archived this page on the web
The information on this page is for reference only. It was accurate at the time of publishing but may no longer reflect the current state at the Canada Border Services Agency. It is not subject to the Government of Canada web standards.
Executive Vice-President's Transition Binder 2019
CBSA Assessment and Revenue Management Branch (CARMB)
Mandate
The CARM is a major transformation project to modernize the CBSA's commercial systems and business processes used to assess imported goods and manage the associated revenue. While CARM has a significant technology component – it is much more than an IT project. The scope of CARM also encompasses:
- a complete business solution component
- an Innovation component
- project management
- a change enablement component
- governance and oversight
- the downstream managed services solution
Vision statement
The vision of CARM is to deliver a globally-leading customs experience that is customer-centric, facilitates legitimate trade, improves compliance and revenue collection, and contributes to securing the borders of Canada.
Vice-President biography

Lisa Anawati joined the CBSA in as Vice-President of the CBSA CARM Branch.
Prior to joining the CBSA, Lisa was with the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) where she was Acting Deputy Assistant Commissioner, International, Large Business and Investigations Branch. Her other positions at the CRA included Director General, International and Large Business and Director General, GST/HST. Lisa has extensive experience in both GST/HST tax and tax service audit operations.
Lisa has a degree in Business Administration from the University of New Brunswick. She is also a Chartered Professional Accountant / Certified Management Accountant and holds a certificate in Public Sector Leadership and Governance from the University of Ottawa.
Overview of CARM
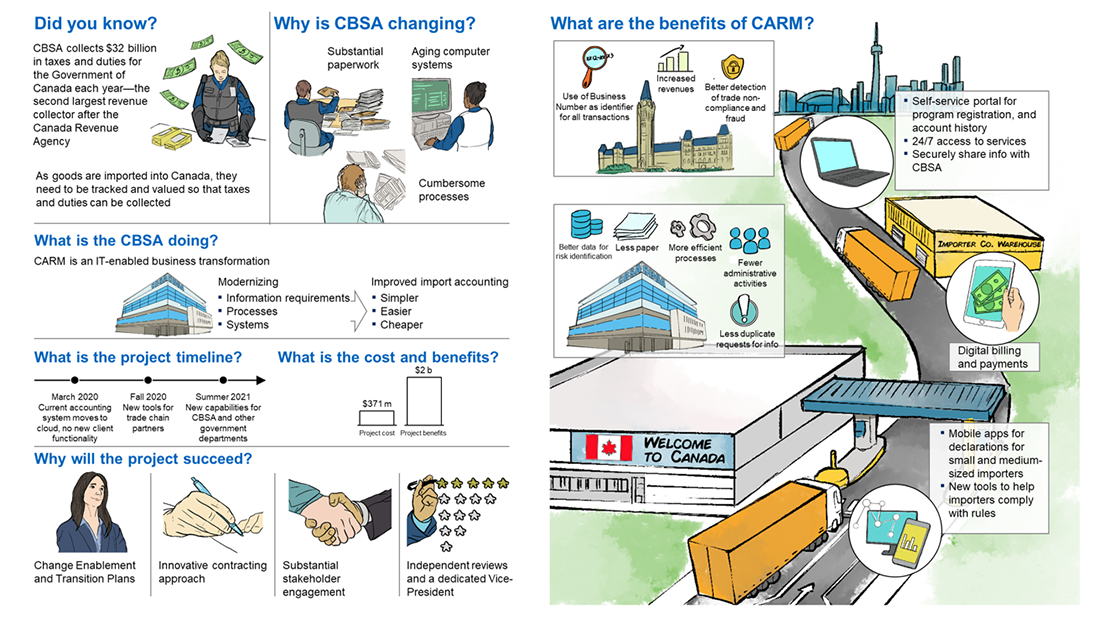
Image description
Did you know?
CBSA collects $32 billion in taxes and duties for the Government of Canada each year-the second largest revenue collector after Canada Revenue Agency.
As goods are imported into Canada, they need to be tracked and valued so that taxes and duties can be collected.
Why is CBSA changing?
CBSA is changing to reduce substantial paperwork, update aging computer systems and alleviate cumbersome processes.
What is the CBSA doing?
CARM is an IT-enabled business transformation: modernizing information requirements, processes and systems which will improve the import accounting making it simpler, easier and cheaper.
What is the project timeline?
- In March 2020, the current accounting system moves to cloud with no new client functionality
- In Fall 2020, new tools for trade chain partners will be implemented
- In Summer 2021, new capabilities for CBSA and other government departments will be implemented
What is the cost and benefits?
The project will cost $371 million and is expected to generate $2 billion.
Why will the project succeed?
The project success is based on change enablement, the development and execution of transitions plans, an innovative contracting approach, substantial stakeholder engagement, independent reviews that will be conducted at different stages of the project as well as on the dedication of its Vice-President.
What are the benefits of CARM?
- CARM will use business numbers as the identifier for all transactions, it will increase revenues and allow better detection of trade non-compliance and fraud.
- CARM will gather better data for risk identification. It will also use more efficient processes requiring fewer administrative activities. It will reduce the use of paper and the number of duplicate requests for information.
- CARM will have a Self portal for program registration, and account history with a 24/7 access to services. Furthermore, all the Portal information will be securely share with the CBSA.
- CARM will allow Digital billing and payments.
- CARM will have mobile apps for declarations for small and medium sized importers as well as new tools to help importers comply with the rules.
CARM includes 18 core processes
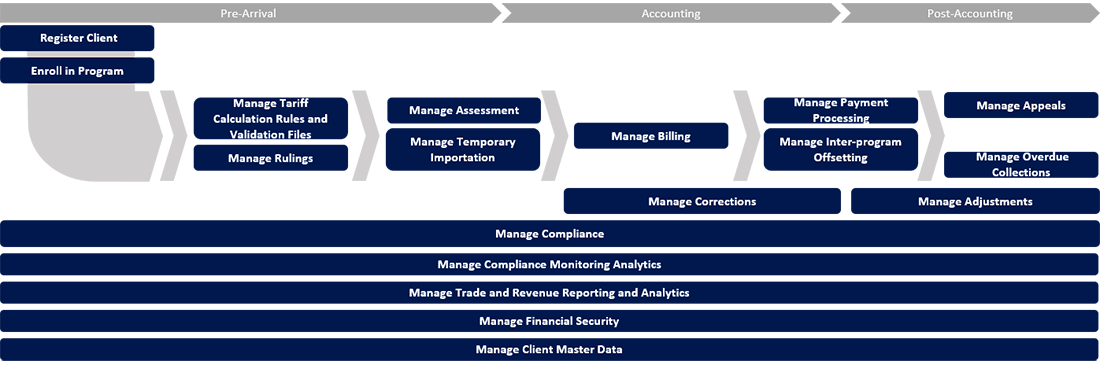
Image description
This graphic provides an overview of the 18 CARM core processes occurring at the 3 different stages of the commercial continuum, including Pre-Arrival, Accounting and Post-Accounting. 9 of the processes occur only at one of the commercial continuum stages, 4 can occur at two different stages and 5 occur at all 3 stages. Listed below are the 3 stages of the commercial continuum and the related core processes.
Stage 1: Pre-Arrival
- Register Client
- Enroll in Program
- Manage Tariff Calculation Rules and Validation Files
- Manage Rulings
- Manage Assessment
- Manage Temporary Importation
- Manage Compliance
- Manage Compliance Monitoring Analytics
- Manage Trade and Revenue Reporting and Analytics
- Manage Financial Security
- Manage Client Master Data
Stage 2: Accounting
- Manage Billing
- Manage Corrections
- Manage Payment Processing
- Manage Inter-program Offsetting
- Manage Compliance
- Manage Compliance Monitoring Analytics
- Manage Trade and Revenue Reporting and Analytics
- Manage Financial Security
- Manage Client Master Data
Stage 3: Post-Accounting
- Manage Payment Processing
- Manage Inter-program Offsetting
- Manage Appeals
- Manage Overdue Collections
- Manage Adjustments
- Manage Compliance
- Manage Compliance Monitoring Analytics
- Manage Trade and Revenue Reporting and Analytics
- Manage Financial Security
- Manage Client Master Data
Work streams
The CARM Branch is comprised of four (4) divisions and nine (9) work streams operational throughout the implementation stage, beginning and to be completed in . The project work streams, in combination with its service delivery partners include the following:
- Change Enablement: includes planning and execution of activities and development of products to enable all CARM stakeholders (internal, external and Other Government Departments (OGD)) to make the required changes, adopt the new roles/processes and use the new tools/solutions of CARM. Change Enablement is comprised of Stakeholder Engagement, Training and Business Readiness and Program Authority.
- Project Control Office: includes planning and execution of project management activities focused on the performance of the CARM project as defined in the project charter and according to the CARM Project Management Plan (scope, schedule, budget, quality, etc.). Vendor relationship management activities focused on the performance and quality of products and services delivered by the CARM Vendor according to the CARM Contract. Governance and Oversight comprises planning and execution of project governance and oversight activities including CBSA project management framework (PMF) and service lifecycle management framework (SLMF) gating activities. The Project Control Office is comprised of the Project Management Office and Corporate Services.
- Solution Delivery: includes planning and execution of activities related to the application and technology that comprise CARM. This includes design, build, test, conversion, cutover, deployment, and stabilization of the application and infrastructure components of CARM, and as well as definition, design, build and transition to the managed services that comprise the contractor-provided solution-as-a-service. The Solution Delivery is comprised of the Managed Services/Cloud/Security and Solutions.
- Business Delivery: comprises planning and execution (delivery) of the CARM business model and results. Activities including changes to CBSA commercial business processes, and benefits planning and realization activities. The Business Delivery is comprised of Revenue Management and Commercial and Trade.
What CARM is doing
- CBSA has established dedicated leadership for the CARM project. Recognizing the mission-critical nature of the CARM system, in the CBSA appointed a Vice-President for CARM, ensuring consistent day-to-day executive-level attention and focus on the successful delivery of the project.
- The CBSA has engaged a leading global business transformation and technology firm (Deloitte) to work with us on the design, implementation and management of CARM. To date Design stage has been delivered within budget and on schedule.
- CARM will now be hosted in the cloud, rather than in a Shared Services Canada (SSC) data centre. This is considered a more modern solution (the Government of Canada now takes a cloud-first approach to IT projects).
- Investing heavily in stakeholder engagement throughout the Project, including Trade Chain Partners (TCP), OGD, and within CBSA.
- Engaged industry leaders to conduct independents reviews to provide ongoing project health checks, and ensure a consistent emphasis on value-adding activities, and achievement of benefits.
Key deliverables (2019-2020)
Completion of detailed design sessions
Working jointly with Business, Solution Delivery and CBSA Subject Matter Experts, CARM is leading a series of Detailed Design Sessions to resolve open items, identify detailed design considerations and validate any key decisions required for the build and implementation of the CARM solution.
Build preparations for upcoming releases (including)
- Build CARM SAP S/4 HANA environment in the cloud hosting environment and establish secure ground to cloud connection (with SSC)
- Document functional and technical migration and cutover activities
- Executing trial migrations for Accounts Receivable Ledger (ARL) system from SAP ECC to SAP S/4 HANA
Testing and deployment
Coordinate CARM build, test and deployment planning with CBSA ISTB and external stakeholders (SSC, integration with OGD, cloud provider).
Business readiness
Identify Business Readiness Leads from each of the key impacted business areas (e.g. Commercial and Trade). Each Lead will develop their own plan and need to identify resources (i.e. members of their Business Readiness Working Group) to support the execution of that plan.
Implementation and deployment
CARM capabilities are being deployed over three releases, balancing risk, change burden and earliest achievement of benefits.
-
Release 0 – ARL lift and shift
ARL will be re-platform to the latest technology (SAP S/4 HANA) and hosted within the cloud environment. -
Release 1 – Initial online portal
Introduction of the internal portal which will set the foundation for case management; and external portal, which will provide basic functionality for tariff calculation, HS code lookup, account information, payment processing and advance ruling requests. -
Release 2 – Core CARM
Deliver the remaining CARM functionality, which includes the transition of functionality from CBSA legacy systems to the CARM solution.
CARM release plan
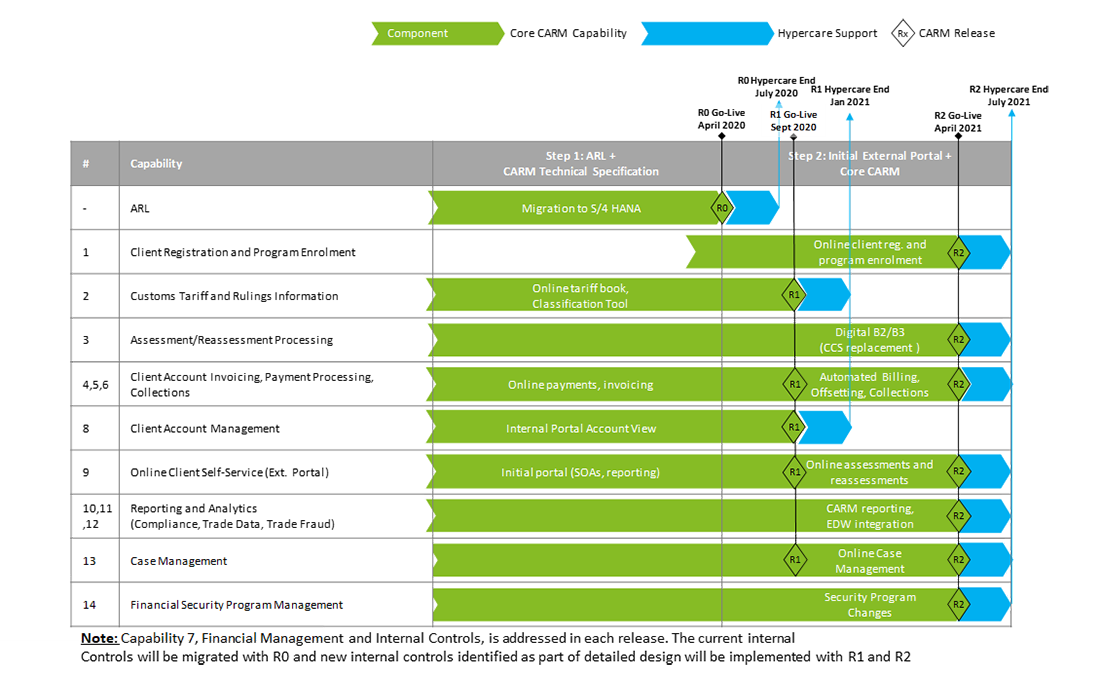
Image description
In the implementation Stage CARM will be deployed in two main phases; the “lift-and-shift” of the ARL system (Release 0) onto the latest s/4 HANA technology, and then an initial release of the External Portal (Release 1) and the release of the full Core CARM capabilities (Release 2).
The table shows each CARM capabilities and the related component(s) planned implementation.
ARL; Migration to S/4 HANA to be deployed in April 2020, Release 0 Go-live followed by an hyper car period ending in July 2020.
1. Client Registration and Program Enrollment to be deployed in April 2021, Release 2 Go-live, followed by an hyper care period ending in July 2021.
2. Customs tariff and rulings information; online tariff book classification tool to be deployed in September 2020, Release 1 Go-live, followed by an hyper care period ending in January 2021.
3. Assessment/reassessment processing; digital B2/B3 (CCS replacement) to be deployed in April 2021, Release 2 Go-live, followed by an hyper care period ending in July 2021.
4, 5, 6. Client account invoicing, payment processing, collections; online payments, invoicing to be deployed in September 2020, Release 1 Go-live. The automated billing, Offsetting, collections to be deployed in April 2021, Release 2 Go-live followed by an hyper care period ending in July 2021.
7. The financial Management and Internal Controls capability, is addressed in each release. The current internal controls will be migrated with R0 and new internal controls identified as part of detailed design will be implemented with Release 1 and Release 2.
8. Client account management: internal portal account view to be deployed in September 2020, Release 1 Go-live followed by an hyper care period ending in January 2021.
9. Online client self-service (external portal); initial portal (SOAs, reporting) to be deployed in September 2020, Release 1. The online assessments and reassessments to be deployed in April 2021, Release 2 Go-live followed by an hyper care period ending in July 2021.
10, 11, 12. Reporting and analytics (compliance, trade data, trade fraud); CARM reporting, EDW integration to be deployed in April 2021, Release 2 Go-live followed by an hyper care period ending in July 2021.
13. Case management; online case management to be deployed in April 2021, Release 2 Go-live followed by an hyper care period ending in July 2021.
14. Financial Security Program Management; Security program changes to be deployed in April 2021, Release 2 Go-live followed by an hyper care period ending July 2021.
CARM governance
The objective of The CARM Project Governance is to support the successful attainment of business outcomes within scope, time and cost by ensuring that appropriate processes and controls for managing the CARM Project are in place. CARM governance will also ensure that accountability for project outcomes is transparent, and that the project conforms to CBSA and GC reporting requirements.
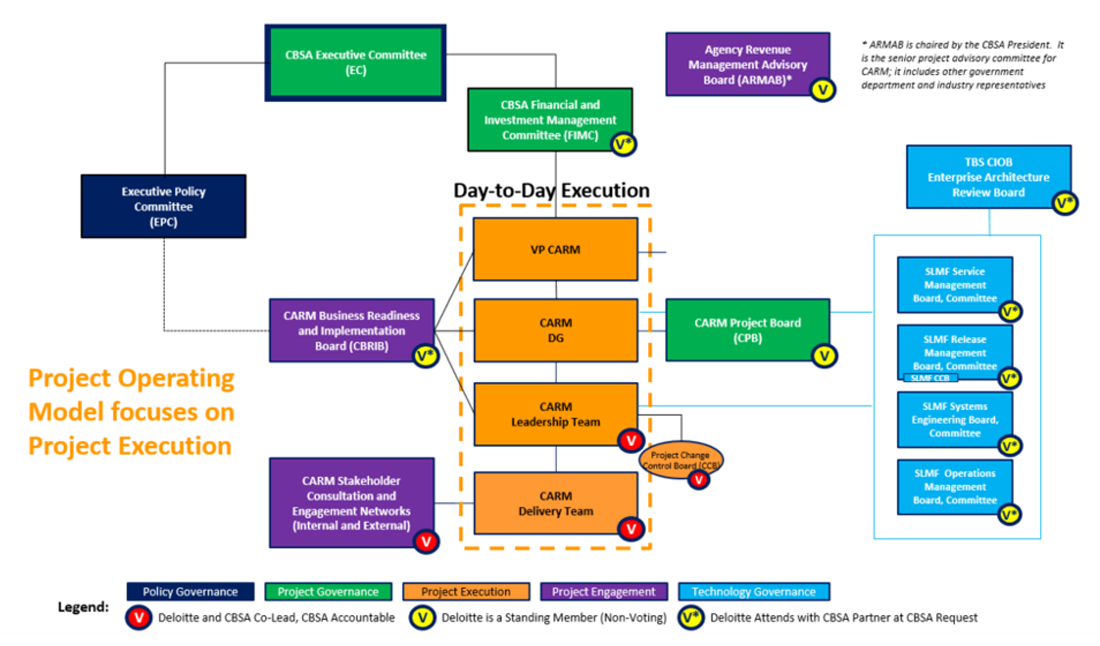
Image description
This graphic provides an overview of the CARM governance structure under the Treasury Board Secretariat oversight. The structure is comprised of 5 type of governance bodies. Project Execution, Project Engagement, Project Governance, Policy Governance and Technology Governance.
The Project Execution, falls under direction of the CARM VP and CARM DG respectively. It consist of a day to day execution which includes, the CARM Delivery Team, the CARM Leadership Team and the Project Change Control Board who are Co-Lead by Deloitte and CBSA and for which CBSA is Accountable.
The Project Engagement consists of the CARM Stakeholders Consultation and Engagement Networks (internal and external) co-lead by Deloitte and CBSA and for which CBSA is Accountable. The CARM Business Readiness Implementation Board led by CBSA and attended by Deloitte on request. The Agency Revenue Management Advisory Board chaired by the President and to which Deloitte is a non-voting standing member. The Agency Revenue Management Advisory Board is the senior project advisory committee for CARM; it includes other government department and industry representatives.
Project Governance includes the CARM Project Board to which Deloitte is a non-voting standing member. The CBSA Financial and Investment Management Committee at which Deloitte attends with CBSA partner at CBSA request and the CBSA Executive Committee.
The Policy Governance consist of the Executive Policy Committee.
Technology Governance includes the SLMF Operations Management Board Committee, the SLMF Engineering Board Committee, SLMF Release Management Board Committee, SLMF Service Management Board and the TBS CIOB Enterprise Architecture Review Board. Deloitte attends with CBSA partner at CBSA request.
CARM's timelines, costs and benefits
Schedule
Costs
$371.5M and $36.5M Ongoing Maintenance including HST
Benefits
- CARM is expected to deliver approximately $2B in total benefits by 2031
- The Net Present Value (NPV) of the CARM project is $594M
- Benefits are expected to begin to accrue in , once implementation is complete:
- Reduced administrative burden for Canadian importers and other trade chain partners, streamlining trade and shifting Canada's global trade enablement ranking, thereby improving Canadian competitiveness and meeting stakeholder expectations
- Increased GC revenues, by enabling improved fairness and consistency in the treatment of all importers, reducing missed opportunities to apply taxes and/or duties, and increasing revenues once complete
- Improved CBSA efficiency, enhancing service and reducing administrative overhead to service delivery while also increasing levels of service and improving CBSA capacity to support open government and improved trade related reporting
Resource profile 2019-2020
[redacted]
Risks
High risk
RSK-1356
Risk CARM net benefits impacted by external stakeholder resistance to CARM changes and/or timelines
Description: Risk that large, diverse external stakeholder population with divergent interests may create resistance to proposed changes that may limit transformation, require unanticipated effort/investment and/or delay implementation, undermining the net benefits of CARM.
Mitigation: Planned CARM Project external stakeholder engagement and communication activities such as TCP Working Groups are being executed as part of the Design Stage activities, and will continue throughout the project. Early escalation to VP and DG CARM of arising concerns.
Rating: 6
Medium risk
RSK-0075
Risk that leg/reg changes will not keep pace with CARM release 2
Description: Risk that regulatory and/or legislative changes desired for CARM cause project delays or delays for implementation of individual capabilities in Release 2 given the long lead time required for leg/reg changes. Program Authority reviews of CARM Release 0 and Release 1 have been completed and have found no regulatory or legislative changes are required for either release.
Mitigation: Additional project resources have been applied to investigate and define approach for changes to policies, regulations, and legislation. Strategic Policy Branch and others socialized of CARM needs. Identification of options and short term work arounds to provide administration relief.
Rating: 4
RSK-1355
Risk internal stakeholders unable to support the amount of change (transformation) within CARM timelines
Description: Risk that internal stakeholders may be unable to support the amount of change (transformation) CARM will bring within the CARM timelines.
Mitigation: Early and continuous engagement with internal stakeholders planned throughout the CARM lifecycle. Development of plans to consider internal stakeholder "change burden" and capacity.
Rating: 3
RSK-1414
Dependency on SSC for ground to cloud
Description: There is a dependency on SSC for ground to cloud. Secure Cloud Enablement and Defense (SCED) (SSC Initiative) will provide a secure ground to cloud connection. SCED is a new initiative, and is planned to be operational by . This aligns to the implementation plan, but no delay can be absorbed.
Mitigation: (Update – ) In the event that Plan A, SCED do not materialize as scheduled, SSC's Plan B, a VPN and/or native Direct Connect is available to test non-protected B data. A decision from CBSA to proceed with Plan B is needed by the end of May due to timing. Team Deloitte has also developed a Plan C, Option – Internet that minimises dependency on SSC. Two other departments dependent on SCED before CBSA.
Rating: 3
- Date modified: