We have archived this page on the web
The information on this page is for reference only. It was accurate at the time of publishing but may no longer reflect the current state at the Canada Border Services Agency. It is not subject to the Government of Canada web standards.
Executive Vice-President's Transition Binder 2019
Information, Science and Technology Branch (ISTB)
Mandate and overview
- The Information, Science and Technology Branch (ISTB) supports the management of Canada's border through the strategic development, application and oversight of information management, technology systems and the delivery of science services
- ISTB is composed of 7 directorates
- ~1,100 employees (as of March 31, 2019) and 228 contractors
- Budget $300 M
- Responsibilities include:
- Information Management
- Enterprise Architecture
- information technology infrastructure and solutions
- planning and portfolio management
- science and engineering
Minh Doan: Vice-President and Chief Information Officer

Mr. Minh Doan was appointed Vice-President of the Information, Science and Technology Branch (ISTB) and Chief Information Officer on January 2, 2018. Since joining the CBSA in 2014 as the Director General of the Business Applications Services Directorate, Minh has also taken on the role of interim Vice-President of ISTB from September 2016 until September 2017 and Director General of Enterprise Architecture, Information Management and Common Services from September to December 2017.
Minh has over 17 years of private and public sector experience in leading enterprise IT projects, improving the efficiency of IT and aligning IT with business operations.
Before joining the CBSA, Minh was an Executive Director at Employment and Social Development Canada where he led major Business and Technology Transformation Projects. Prior to that he worked at the Privy Council Office (PCO) on Administrative Services Review and government-wide IT strategies to transform service delivery to Canadians. He has also held progressively more senior positions at Service Canada and Bell Canada.
Minh has a bachelor's degree in Computer Science from the Université du Québec and a certificate in Leading Change and Organizational Renewal from the Harvard Business School.
Executive team
Minh Doan
Vice-President and Chief Information Officer
Cameron Macdonald
Director General
Business Application Services Directorate
Patrick Mineault
A/Director General
Business, Corporate Projects and Management Portfolio Directorate
Franco Germano
A/Director General
Commercial Portfolio Directorate
Gino Lechasseur
Director General
Enterprise Architecture, Information Management and Common Services Directorate
Daniel Tremblay
Director General
Enterprise Services Directorate
Dave Thompson
Director General
Science and Engineering Directorate
Kelly Bélanger
Director General
Travellers Projects Portfolio Directorate
Supporting CBSA’s vision
- Information, Science and Technology Branch (ISTB) delivers science, engineering, architecture, and Information Management (IM) major projects and Information Technology (IT) services in support of all front-line operational activities
- ISTB supports the delivery of services for the CBSA’s 24/7 business operating environment through:
- Provision of 99.5% availability of CBSA’s mission critical managed systems
- High Availability Response Team, in cooperation with Shared Services Canada (SSC)
- ISTB manages a very complex and highly integrated technology environment that is used by CBSA Border Operations to enforce 90 Acts and Regulations
- 110 mission critical applications
- 183 national applications
- 257 local/regional applications
- 2 independent secure networks
- 19,453 workstations
- 8,320 mobile devices
- 1 science laboratory
- $98M of detection technology, including:
- 17 large scale imaging units
- 39 radiation detection portals
- 125 trace detectors for narcotics
- 155 small scale x-ray units
- 8,500 radios
- ISTB promotes innovation and the rapid adoption of modern and sustainable technological-based solutions
Directorates and core responsibilities
Business Application Services Division (BASD):
Responsible for the development, maintenance and support of IT application solutions related to travellers, enterprise and common services, commercial and corporate.
Business, Corporate Projects and Portfolio Management (BCPPMD):
Responsible for supporting fiscally sound business processes and the achievement of ISTB key initiatives and deliverables through effective and efficient monitoring, reporting and management, including client management, risk management of the portfolio, prioritization and governance and corporate application project management.
Commercial Portfolio Directorate (CPD):
Responsible for delivering IT projects that ensure the safety of Canadians and facilitate commercial trade.
Enterprise Architecture, Information Management and Common Services (EAIMCS):
Responsible for providing the holistic Information Management (IM) and Enterprise Architecture (EA) programs for the Agency. In addition, this Directorate is responsible for supporting the Agency’s Data Analytics program and enabling Business Collaboration. The EA Program also includes the development and maintenance of the CBSA Reference Architecture (CBSA blueprint) used across the Agency.
Enterprise Services Directorate (ESD):
Responsible for the Agency’s IT infrastructure and services supporting the effective delivery of technology products, applications and services to meet business needs, while ensuring the integrity and availability of all technology infrastructure.
Science and Engineering (S&E):
The authority for science and engineering activity within the CBSA, and ensures that the Agency fully and smartly leverages science and technology by keeping abreast of and sharing new developments and best practices, applying a scientific lens to business challenges, and practicing due diligence in the application of science and engineering within a border management context.
Travellers Projects Portfolio Directorate (TPPD):
Responsible for delivering IT projects that ensure the safety of Canadians and facilitate travel.
How technology support is organized
Client services for major IT project management are aligned to the CBSA’s business: Travellers, Commercial, Intelligence and Enforcement, Corporate, and Common Services.
Traditional IM/IT functions:
- IM/IT Program and Business Management (Vice-President/Chief Information Officer)
- Information Management Programs
- Business Applications and Solutions Development and Maintenance
- Enterprise Services and IT Operations
- Planning, Portfolio Management and Client Services
Science and Engineering functions:
- Science and engineering support and operations
- Analytical and Forensic Services
- Border Technology and Research and Development Program
Enterprise Architecture functions:
Supporting all 17 DRF programs and internal services, including business, data/information, applications, technology, security and privacy domains.
Operating environment: Key partners and stakeholders
- ISTB works closely with key partners and stakeholders to deliver CBSA systems and services:
- Shared Services Canada (SSC): projects, data centre operation services, network services, email and voice communications services
- Canada Revenue Agency (CRA): CBSA regional IT support, Canada-wide IT help desk support, Corporate Administrative Systems support and development
- Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC): line-of-business application support and projects
- Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP): line-of-business application support
- Border Five (B5): Interoperability with partners
- A complex data communications environment with:
- Other government department partners
- External private sector clients and stakeholders
- Other domestic partners and foreign government entities
Major deliverables for fiscal year 2019 to 2020
Information Technology (IT) organization
Deliverable 1: Cloud strategy
Develop Cloud Strategy for the Agency; will support closure of St. Laurent Data Centre by 2023
Deliverable 2: Workload migration
Migration of all CBSA assets and services out of Shared Services Canada’s (SSC’s) Data Centre St. Laurent (DCSL) and Centre des Données Ouest Québec (CDOQ) before March 2023
Deliverable 3: Windows 10 migration
Migration of over 14,000 devices from outdated operating systems to Windows 10 before end of support in January 2020
Deliverable 4: Microsoft server 2016 upgrade
Mandatory operating system upgrades for all Windows servers before end of support in January 2020
Travellers projects
Interactive advance passenger information
- Fully implemented and functioning as designed
- With the final production reporting scheduled for January to March 2019, project close-out can be completed by August to September 2019
Biometrics expansion
- On July 31, 2018, CBSA implemented expanded fingerprint verification at Secondary at 11 air and 38 land Ports of Entry (POEs), and introduced biometric enrolment at Secondary at 19 air and 38 land POEs
- Information sharing commenced November 2015 with Australia and New Zealand; United Kingdom on hold
- In March 2018, CBSA completed Generic Passage Flow (previously Universal Passage) high-level business requirements analysis. Remainder of scope to be completed outside of Biometrics Expansion Project
- Systematic Fingerprint Verification at Primary underway at Canada’s airports
Entry/Exit
- Information related to the movement of people in and out of Canada
- Mobile primary inspection application completed and handheld devices fully deployed to 72 remote land ports
- Next Generation Mobile Devices being evaluated
- C-21 legislation passed December 2018
- Regulations for Land (US exchange) and Air scheduled for June 2019 and June 2020 respectively
- Full systems implementation scheduled to be completed by Spring 2020
- Commercial Air Carriers onboarding scheduled for completion by Spring 2021
- Final production reporting and onboarding to enterprise Service Oriented Architecture in Winter 2020
- Radio Frequency Identifier Phase 4 Project is completed development and planned for production in Quarter 1, Fiscal year 2019 to 2020
- Will enable capability to read Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) enabled travel documents issued by the U.S. so risk assessment can be completed prior to the traveller presenting to a Border Services Officer (BSO)
- Implementing a Passage Fuzzy Search solution to deliver advanced Traveller and passage query capabilities to BSOs at Secondary in pilot mode during spring 2019
- Pilot will be evaluated prior to full production deployment
Primary Inspection Kiosk
- Designed to optimize passenger flow through next generation kiosks
- Allows increased processing of passengers
- First deployment occurred March 2017
- All major airports except Toronto T1 and Calgary are implemented
- Plan to integrate eDeclaration mobile application with Commercial Air carrier’s mobile application
Passenger Protect Program centralized screening
- CBSA will vet air carrier passenger data against Public Safety’s “No Fly List” for suspected terrorists
- Planning Phase (requirements gathering, design, cost refinement) completed in fiscal year 2018 to 2019
- Execution Phase will commence in fiscal year 2019 to 2020 with air carrier onboarding beginning in September 2020
NEXUS integration into Primary Inspection Kiosks
Building on the implementation of the Primary Inspection Kiosks, looking to integrate NEXUS into Primary Inspection Kiosks and adding facial biometrics.
Gender designation
Changes to CBSA systems to support implementation of a Government of Canada Policy Framework for gender designation potentially impacting the collection of gender data and introduction of an additional gender marker.
Commercial projects
eManifest
- Project scheduled to close in Quarter 2 2019 to 2020
- System changes scheduled from Quarter 3 2018 to 2019 to fiscal year 2020 to 2021 to stabilize electronic house bill reporting and risk assessment to support integrated decision model
Postal Modernization Initiative
- Initially implemented in Vancouver in May 2014, it is currently being redeveloped
- This initiative provides Border Services Officers (BSOs) in Vancouver with enhanced processes, systems and detection technology to clear mail
- Planning and development underway for the Montreal and Toronto Mail Centres (Montreal deployment anticipated Quarter 1 of fiscal year 2020 to 2021
- Toronto deployment anticipated for Quarter 2 of fiscal year 2020 to 2021)
Secure Corridor Concept
- Lane equipped with sensors and technology to process carriers remotely
- Minimized time to process “trusted/pre-cleared” carriers by leveraging technology
- Advanced border technologies (RFID, sensors, multiple camera views (driver, license, trailer), voice intercom communication) interact with Primary Inspection Line (PIL) system and a central work station to facilitate Border Services Officer processing
- Pilot of Phase 1 (September 2018) using one PIL lane at Windsor’s Ambassador Bridge POE to process a limited number of commercial low-risk trusted traders to demonstrate and confirm the use of advanced border technologies
- The objective is to reduce PIL processing times in order to improve border wait times
- Phase 2 is planned for 2019 to 2020 and will introduce a system connection to existing CBSA systems ACROSS and Integrated Primary Inspection Line (IPIL)
- Phases 3 and 4 will expedite passage for Customs Self-Assessment at PIL
Science and Engineering (S&E) projects
Two-way radio modernization
- Phased replacement of Personal Alarm Security System (PASS) radio equipment with digital encrypted radio solutions
- Procurement of $15M in digital encrypted radios completed in fiscal year 2017 to 2018
- Beginning in 2018, gradual migration of two-way radio communication to wide-area, secure, Public Safety interoperable radio networks
- Upgrade of the CBSA Metro Vancouver radio communication system and interconnecting with Prince Rupert operations between 2017 and 2019
Tailorable Operational Picture System (TOPS) data visualization proof of concept
- TOPS is a prototype of an information visualization tool developed in 2017
- Provides an interactive view of border operations by combining visual interfaces, advanced analytical functions and multiple data sources
- Allows rapid, flexible and intuitive data analysis for the improvement of border management processes
- A pilot took place in Quarter 3 2018 to 2019 in the Northern Ontario Region to determine the value of a data visualization and analytics platform at POEs
Voice Reporting System (part of Alternative to Detention Program)
- The pilot that began in the Greater Toronto Region has now been rolled out nationally with more than 800 individuals enrolled
- Individuals report to the CBSA via telephone using an automated system that confirms their identity using voice biometrics and records their location when calling from a cellular phone
- Consistent, risk-based national program with persons treated fairly and commensurate with risk
Roberts Bank Marine Container Examination Facility (Vancouver)
- Specification, procurement, installation, and commissioning of a next generation pallet imaging system and other detection technologies
- Specification Fixed Site Large-scale Imaging system
- Providing expedited transfers to secondary examination site and minimizing carrier’s costs
Opioids Crisis Initiative
- Supporting CBSA’s Programs Branch in the rollout of over 60 Designated Safe Examination Areas
- Based on recently completed pilot at Vancouver International Mail Centre (VIMC),will be setting up permanent Designated Safe Sampling Areas (satellite laboratories) in Vancouver, Montreal and Toronto
- Contributing to Border Services Officers’ health and safety, while facilitating enforcement activities
Guns and Gangs Initiative
- Evaluation and procurement of hand-held X-ray detection technology
- Specification, procurement, installation, and commissioning of pallet imaging systems in airports
- Increasing Border Services Officers’ ability to perform timely inspection of air cargo/courier commodities
Other Information, Science and Technology Branch (ISTB) project involvement
Advanced analytics
- Increasing the use of Open Source advanced analytics capabilities to facilitate the exchange of risking algorithms with Border Five (B5) partners
- Using data architecture and data quality analysis to improve the quality of data being used for assessing trade and travel risk
Geospatial analytics service upgrades
- Increasing investment in geospatial analytics capabilities to add data visualization to Port of Entry situational awareness
- Use geospatial technologies as the proof of concept in migrating to more modern, cloud-based technologies for advanced analytics
Recourse Content Management System (RCMS): Case management (GCCase) pilot
- Planning and design is underway and will complete in fiscal year 2018 to 2019 with development and implementation in fiscal year 2019 to 2020
- New solution will onboard GC Case platform
- Combining both existing Recourse systems into one Case Management system
(PAXIS) Stabilization and optimization: Phase 2
- Phase 2 is underway and will be completed in fiscal year 2019 to 2020
- Optimized solution will bring stability to PAXIS by performing preparatory work for the consolidation of flight acquittal activities that are currently in PAXIS and will be moved to Acquittal and Compliance Service (ACS)
Upcoming / “on the radar” projects: Travellers
Known Travellers Digital Identity (KTDI)
- Canada and the Netherlands announced at a recent World Economic Forum that they will explore integrating new and emerging digital technologies into the components of the air travel continuum
- KTDI is designed to be a user-driven, digital identity that is biometrically-anchored and over time facilitates quick and document-less travel
Travellers Entry Processing System replacement
- Installed at approximately 230 CBSA sites nationally
- 98% of all traveller revenue is collected through this system
Generic Passage Flow
Refers to the future state of border processing and will address the complete border processing continuum from a traveller perspective.
Reporting Offsite Arrival: Mobile (ROAM)
ROAM will be deployed at small Canadian Ports of Entry.
Customs Processing Center System (CPCS) System replacement
- Planning and design is underway and will complete in fiscal year 2019-20 with development and implementation in fiscal year 2020 to 2021
- New solution will integrate with CARM
Upcoming / “on the radar” projects: Commercial
Commercial Trusted Trader Program membership service enhancements
Enhance Highway Carrier harmonization of the CBSA Partners in Protection and the U.S. Customs and Border Protection
Commercial Risk Assessment and Commercial Data Acquisition and Notification service enhancements
- Enhancements to deliver a centralized risk-processing model with an end-to-end view of shipment information
- Evolve the commercial risk assessment process from a transactional risk model to a model that includes data analytics
Canadian Export Reporting System
- New online automated export reporting system will replace the Customs Automated Export Declaration
- Target production date is December 2019
Other “on the radar” projects
Dynamic risking
Predictive analytics will be used to assign compliance scores for all travellers entering Canada, which will be relayed to Border Services Officers and support at-border decision making. This will result in fewer and faster interactions with low-risk travellers and direct CBSA activities toward higher-value returns.
Image and network/graph analytics, and data visualization toolset
- Using image analytics to better detect threats across lines of business, such as postal packages, large-scale imaging, or traveller biometrics
- Using network analytics to identifiscal year previously unknown relationships that could inform risk levels in either trade or travel
Trusted digital identity
Significant investment in business and data architecture to ensure data are collected once and reused to ensure higher integrity in the data used to manage the border.
Autonomous and connected vehicles
- Ensuring readiness to meet the challenges of advances in the transportation sector that can significantly modifiscal year the risk profile of traffic at the border
- Monitoring the advances in drone-based deliveries that could affect how the CBSA manages trusted programs
GC Case
The migration of CBSA Case Management systems to the GC Case platform has begun.
Workforce profile
The following workforce and demographic information is draft information, provided by the Human Resources Branch.
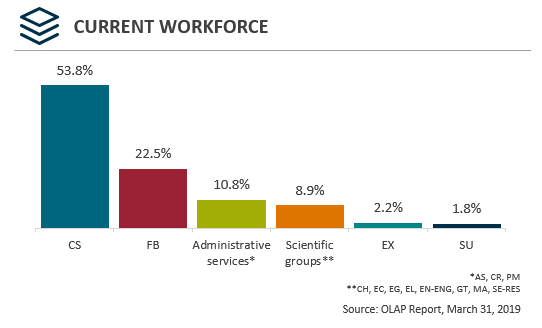
| Group | Number of employees | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| AS | 65 | 6.5% |
| CH | 41 | 4.1% |
| CR | 41 | 4.1% |
| CS | 536 | 53.8% |
| EC | 1 | 0.1% |
| EG | 15 | 1.5% |
| EL | 8 | 0.8% |
| EN | 10 | 1.0% |
| EX | 22 | 2.2% |
| FB | 224 | 22.5% |
| GT | 1 | 0.1% |
| MA | 5 | 0.5% |
| PM | 2 | 0.2% |
| SE | 8 | 0.8% |
| SU | 18 | 1.8% |
| Total | 997 | 100.0% |
Quick facts
- 45.6 years is the average age of the current ISTB workforce
- 76.3% of employees are in the CS and FB occupational groups
- 40.2% of ISTB's workforce are women compared to 46.8% (average CBSA women representation)
Source: OLAP Report, March 31, 2019, and Q4 2018-2019 Employment Equity Report, April 1, 2019
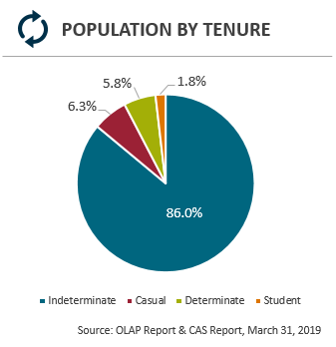
Population by tenure
- Indeterminate: 86%
- Casual: 6.3%
- Determinate: 5.8%
- Students: 1.8%
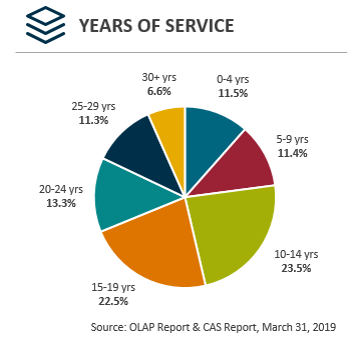
Years of service
- 0-4 years: 11.5%
- 5-9 years: 11.4%
- 10-14 years: 23.5%
- 15-19 years: 22.5%>
- 20-24 years: 13.3%
- 25-29 years: 11.3%
- 30+ years: 6.6%
Demographic information
Directorate overview by gender
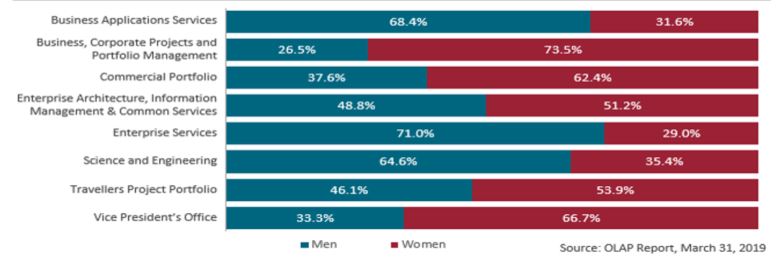
Directorate overview by gender: By quickly looking at the graph, it may seem that there are more women than men in ISTB’s workforce. However, there are more men than women in two (2) of ISTB’s biggest directorates (BASD: 173 men vs 80 women; ESD: 198 men vs 81 women), explaining the minority of women within the entire branch. Women are also underrepresented in ISTB compared to CBSA’s average representation of women.
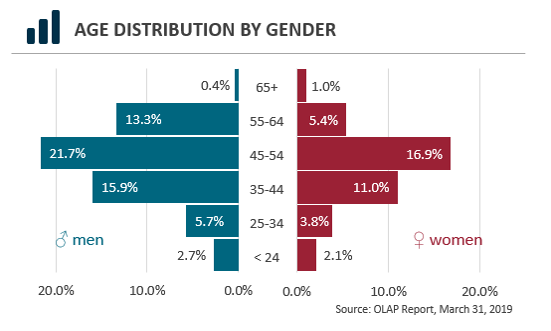
Age distribution by gender: There is a need to rejuvenate the workforce as approximately 14% of ISTB’s workforce is under 34 years of age. 59% of its workforce is 45 years old and over, meaning that a great percentage of its workforce is likely to retire within the next 10 years.
Employment equity
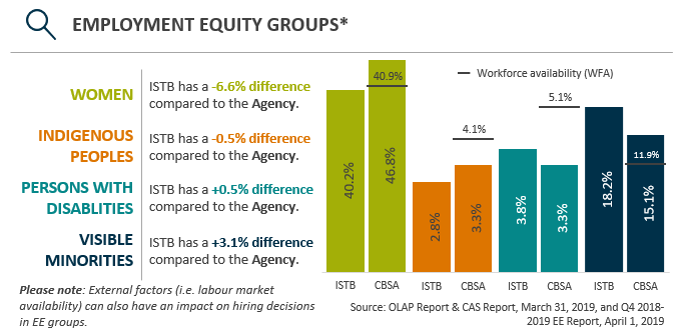
Please note: External factors (for example labour market availability) can also have an impact on hiring decisions in employment equity groups.
| ISTB | CBSA | Percentage difference between ISTB and CBSA |
Workforce availability rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women | 40.2% | 46.8% | −6.6% | 40.9% |
| Indigenous Peoples | 2.8% | 3.3% | −0.5% | 4.1% |
| Persons with disabilities | 3.8% | 3.3% | +0.5% | 5.1% |
| Visible minorities | 18.2% | 15.1% | +3.1% | 11.9% |
Source: OLAP Report and CAS Report, March 31, 2019, and Quarter 4 2018 to 2019 Employment Equity Report, April 1, 2019
The Graph above shows the percentage of specific Employment Equity groups employed by the Information, Science and Technology Branch and the Canada Border Services Agency compared to the workforce availability of these groups.
Women: Workforce availability is 40.9%. 40.2% of Information, Science and Technology Branch’s employees are women. 46.8% of Canada Border Services Agency’s employees are women.
Indigenous Peoples: Workforce availability is 4.1%. 2.8% of Information, Science and Technology Branch’s employees are Indigenous Peoples. 3.3% of Canada Border Services Agency’s employees are Indigenous Peoples.
Persons with disabilities: Workforce availability is 5.1%. 3.8% of Information, Science and Technology Branch’s employees are persons with disabilities. 3.3% of Canada Border Services Agency’s employees are persons with disabilities.
Visible minorities: Workforce availability is 11.9%. 18.2% of Information, Science and Technology Branch’s employees are visible minorities. 15.1% of Canada Border Services Agency’s employees are visible minorities.
Employee departure information
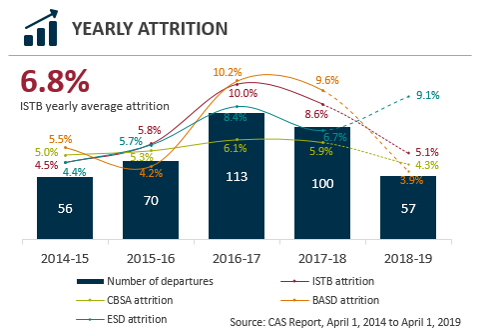
| 2014 to 2015 | 2015 to 2016 | 2016 to 2017 | 2017 to 2018 | 2018 to 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of departures | 56 | 70 | 113 | 100 | 57 |
| CBSA attrition | 5.0% | 5.3% | 6.1% | 5.9% | 4.3% |
| ISTB attrition | 4.5% | 5.8% | 10.0% | 8.6% | 5.1% |
| ESD attrition | 4.4% | 5.7% | 8.4% | 6.7% | 9.1% |
| BASD attrition | 5.5% | 4.2% | 10.2% | 9.6% | 3.9% |
Source: CAS Report, April 1, 2014 to April 1, 2019
The yearly attrition graph summarizes the total attrition and attrition rate of all of the Canada Border Services Agency, the Information, Science and Technology Branch, and two Information, Science and Technology Branch directorates (Enterprise Services Directorate and Business Application Services Directorate). It provides yearly figures between 2014/2015 to 2018/2019.
2014 to 2015: There were 56 total departures from the Information, Science and Technology Branch. Canada Border Services had an attrition rate of 5%. The Information, Science and Technology Branch had an attrition rate of 4.5%. The Enterprise Services Directorate had an attrition rate of 4.4%. The Business Applications Services Directorate had an attrition rate of 5.5%.
2015 to 2016: There were 70 total departures from the Information, Science and Technology Branch. Canada Border Services had an attrition rate of 5.3%. The Information, Science and Technology Branch had an attrition rate of 5.8%. The Enterprise Services Directorate had an attrition rate of 5.7%. The Business Applications Services Directorate had an attrition rate of 4.2%.
2016 to 2017: There were 113 total departures from the Information, Science and Technology Branch. Canada Border Services had an attrition rate of 6.1%. The Information, Science and Technology Branch had an attrition rate of 10%. The Enterprise Services Directorate had an attrition rate of 8.4%. The Business Applications Services Directorate had an attrition rate of 10.2%.
2017 to 2018: There were 100 total departures from the Information, Science and Technology Branch. Canada Border Services had an attrition rate of 5.9%. The Information, Science and Technology Branch had an attrition rate of 8.6%. The Enterprise Services Directorate had an attrition rate of 6.7%. The Business Applications Services Directorate had an attrition rate of 9.6%.
2018 to 2019: (Please note some departure data has not yet been captured for fiscal year 2018 to 2019). There were 57 total departures from the Information, Science and Technology Branch. Canada Border Services had an attrition rate of 4.3%. The Information, Science and Technology Branch had an attrition rate of 5.1%. The Enterprise Services Directorate had an attrition rate of 9.1%. The Business Applications Services Directorate had an attrition rate of 3.9%.
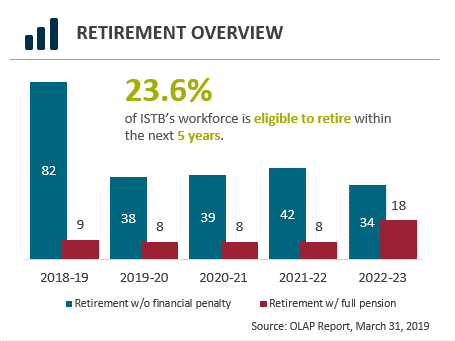
23.6% of ISTB’s workforce is eligible to retire within the next 5 years.
| Type of retirement | 2018 to 2019 | 2019 to 2020 | 2020 to 2021 | 2021 to 2022 | 2022 to 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retirement without financial penalty | 82 | 38 | 39 | 42 | 34 |
| Retirement with full pension | 9 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 18 |
Source: OLAP Report, March 31, 2019
The retirement overview graph summarizes the status of employees eligible to retire in the Information Science and Technology Branch within the next 5 years. Overall, 23.6% of the Information, Science and Technology Branch’s employees will be eligible to retire in the next 5 years.
In 2018 to 2019, 82 employees will be eligible to retire without financial penalty. 9 employees will be eligible to retire with a full pension.
In 2019 to 2020, 38 employees will be eligible to retire without financial penalty. 8 employees will be eligible to retire with a full pension.
In 2020 to 2021, 39 employees will be eligible to retire without financial penalty. 8 employees will be eligible to retire with a full pension.
In 2021 to 2022, 42 employees will be eligible to retire without financial penalty. 9 employees will be eligible to retire with a full pension.
In 2022 to 2023, 34 employees will be eligible to retire without financial penalty. 18 employees will be eligible to retire with a full pension.
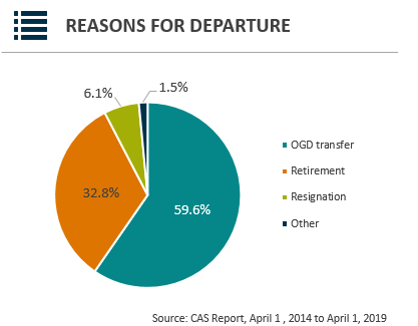
| Reasons for Departure | Percentages |
|---|---|
| OGD transfer | 59.6% |
| Retirement | 32.8% |
| Resignation | 6.1% |
| Other | 1.5% |
Reasons for Departure: The Reasons for Departure pie chart shows the percentages of reasons for employee departure from the Information, Science & Technology Branch between April 2014 and April 2019.
- Date modified: